Atopic Dermatitis: A Case Study
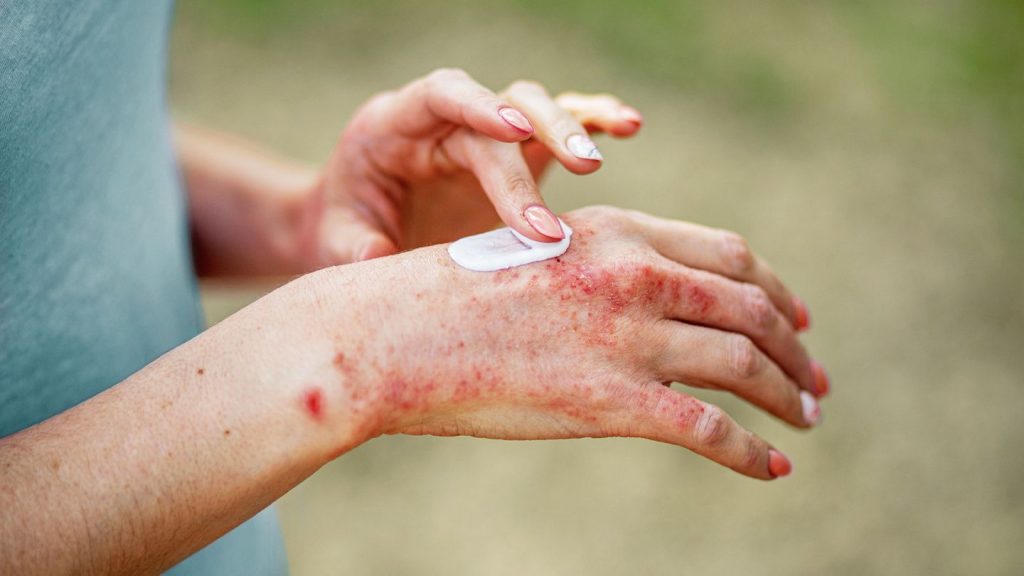
Atopic dermatitis is a prevalent skin condition characterized by chronic inflammation and intense itching. It affects approximately 15-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and distress.
In a recent study, UVB therapy was found to significantly improve the quality of life for patients with atopic dermatitis by reducing itching and rash severity. Patients also reported a decrease in sleep disruptions and overall improvement in well-being after receiving UVB treatment.
Additionally, long-term studies have shown that UVB therapy can lead to sustained remission of symptoms in some patients with atopic dermatitis, making it a promising treatment option for those struggling with this condition.
Overall, UVB therapy has shown great potential in managing the symptoms of atopic dermatitis and improving overall skin health for affected individuals. Further research and development in this area could lead to more effective treatment options for patients living with this challenging skin condition. So, UVB treatment can be a viable option for people suffering from atopic dermatitis, and it is important to explore its effectiveness as a treatment method further. By understanding the benefits and limitations of UVB therapy, we can continue to improve our approach to treating skin conditions and provide better care for those who need it. With ongoing advancements in medical technology and research, there is hope for finding more efficient and reliable ways to manage atopic dermatitis and other skin conditions in the future.
An In-Depth Exploration of UVB Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition marked by episodes of severe itching, redness, and discomfort. It has a significant impact on quality of life, affecting both children and adults worldwide. With the rise in the prevalence of atopic dermatitis, effective management strategies are of paramount importance.
One promising treatment is ultraviolet B (UVB) phototherapy, known for its immunomodulatory effects that can help manage the symptoms of AD.
Understanding UVB Phototherapy
UVB phototherapy involves the use of a specific wavelength of ultraviolet light to treat skin conditions. For atopic dermatitis, narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) is most commonly used due to its efficacy and safety profile. NB-UVB emits wavelengths between 311-313 nanometers, which are beneficial in reducing inflammatory responses in the skin. The exposure to UVB light leads to a decrease in the overactive immune cell activities that contribute to inflammation and skin barrier disruption.
Mechanism of Action
UVB therapy works by inducing photochemical reactions in the skin. One of the primary effects is the reduction in Langerhans cells, a type of dendritic cell that presents antigens to T-cells, thereby dampening the immune response that leads to inflammation. Additionally, UVB treatment encourages the production of vitamin D derivatives in the skin, which play a role in modulating immune function. By restoring normal skin barrier function and reducing inflammatory cytokines, UVB helps in alleviating the symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
Clinical Efficacy
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of UVB therapy for managing atopic dermatitis. Patients often experience a significant reduction in pruritus, erythema, and lichenification. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology highlighted that patients receiving NB-UVB therapy reported substantial improvement in their quality of life. These patients experienced fewer flares and less severe symptoms over time, making UVB phototherapy a viable long-term management option.
Treatment Protocols
A typical UVB treatment regimen for atopic dermatitis involves sessions several times a week in a controlled clinical setting. The duration and frequency depend on the severity of the condition and the patient’s response to treatment. Physicians carefully monitor the exposure time to minimize the risk of adverse effects like burns. Incremental increases in exposure based on the skin type and response are critical in optimizing treatment outcomes.
Safety and Side Effects
Despite being a beneficial treatment option, UVB therapy is not without risks. The most common side effect is skin erythema resembling mild sunburn, which typically resolves quickly. Long-term UVB exposure can lead to an increased risk of skin cancer and photoaging, although NB-UVB is considered safer than other UV therapies due to its targeted wavelength range. Regular dermatologist visits and careful monitoring help mitigate these risks significantly.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
UVB phototherapy is generally considered cost-effective, especially when compared to systemic immunosuppressive therapies. However, its accessibility can be a challenge for some patients due to the need for frequent clinic visits. The development of home phototherapy devices has emerged as a solution, allowing patients to administer treatment under medical supervision in the comfort of their homes. This advancement could further increase the accessibility of UVB treatment for broader populations.
Comparative Analysis with Other Treatments
Compared to topical therapies and systemic medications, UVB therapy offers unique advantages in terms of reducing itch and inflammation effectively. While topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors are often the first line of defense in managing atopic dermatitis, they can have significant side effects with long-term use. Systemic therapies like cyclosporine are usually reserved for severe cases due to their immunosuppressive nature and associated risks. UVB phototherapy provides an alternative that can be used in conjunction with or as a replacement for these therapies, depending on individual patient needs.
Psychological Impact and Quality of Life
Atopic dermatitis not only affects physical health but also has profound psychological impacts, often leading to anxiety, depression, and social isolation in affected individuals. The improvement in skin condition through UVB therapy has been correlated with enhanced emotional well-being and reduced psychological stress, underscoring the holistic benefits of this treatment method.
Future Prospects and Research
Ongoing research aims to refine UVB therapy protocols, enhance efficacy, and reduce side effects. Studies are exploring optimal dosing schedules, combination therapies with biologics, and new technologies to improve treatment administration. The advent of personalized medicine may soon allow for tailored UVB treatment approaches based on genetic and epigenetic factors, optimizing patient outcomes while minimizing risks.
Conclusion
UVB phototherapy represents a cornerstone in the management of atopic dermatitis, offering a balance of efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness. As research continues to advance, it is likely that UVB therapy will maintain and expand its role in therapeutic strategies for atopic dermatitis. With improved accessibility and understanding, patients can receive more targeted care that addresses both the physical symptoms and psychological burdens of this challenging condition. The integration of UVB treatment into comprehensive care plans highlights its value as a critical tool in improving the lives of those with atopic dermatitis.
The journey of atopic dermatitis management is ever-evolving, with UVB therapy playing an integral role. Its continued development, supported by rigorous research and technological advancements, promises a brighter future for individuals seeking relief from this enduring skin condition.

Silvia Malgot is a renowned author and expert in the fields of skincare and beauty, with over a decade of experience researching and writing about effective treatments, holistic approaches, and innovative technologies. Her passion for empowering individuals to feel confident in their own skin has driven her to explore cutting-edge solutions and timeless traditions in skincare.
Silvia has contributed to several leading health and beauty publications, providing insights into trends, product recommendations, and practical advice grounded in science. Her approachable yet detail-oriented style has made her a trusted voice for readers seeking clarity in an overwhelming industry. When she’s not writing, Silvia actively participates in workshops and seminars, sharing her knowledge and inspiring others to prioritize self-care through sustainable, informed practices.