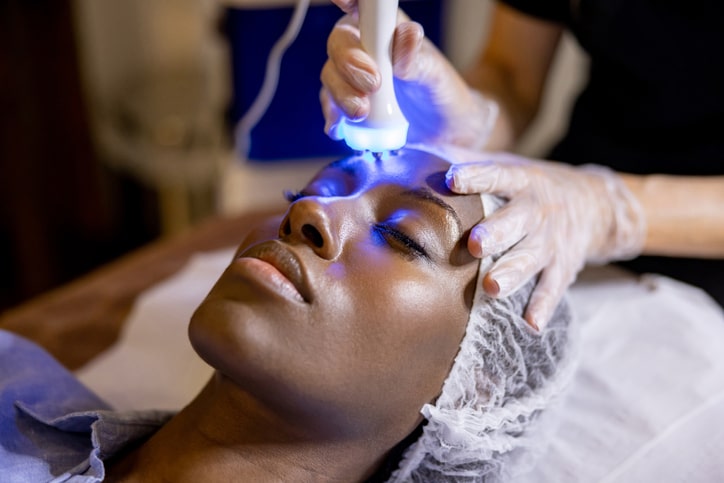
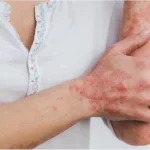
Ultraviolet B UVB therapy has emerged as a prominent treatment option for various skin conditions, including psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo. As an effective non-invasive treatment, UVB therapy utilises specific wavelengths of ultraviolet light to target affected areas of the skin, promoting healing and symptom relief. However, for potential patients considering this therapy, the crucial question remains—Is UVB therapy FDA eligible? In this exploration, we will discuss the FDA’s role in evaluating UVB therapy, the effectiveness of the treatment, and what patients need to know about its eligibility and safety standards.
Understanding UVB Therapy
UVB therapy involves the controlled exposure of the skin to UVB light, typically delivered through specialized lamps or phototherapy units. The treatment works by selectively targeting skin cells, reducing inflammation, and slowing down the excessive growth of skin cells—a hallmark of many dermatological disorders. This therapeutic approach can vary in intensity and duration depending on the specific condition being treated.
Mechanism of Action
UVB light penetrates the skin and interacts with the cells, increasing the production of vitamin D while reducing hyperactivity in immune responses responsible for skin conditions. By suppressing the inflammatory processes and normalising skin cell production, UVB therapy promotes significant improvements in skin health for many patients.
FDA Approval Process
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in determining whether medical devices, including the light sources used in UVB therapy, meet the necessary safety and efficacy standards before being marketed to the public. The FDA categorises devices based on the risks they pose to patients and their intended use.
Classifications of Medical Devices
The FDA classifies medical devices into three categories:
- Class I: Low-risk devices, subject to the least regulatory control.
- Class II: Moderate-risk devices, requiring greater regulatory oversight.
- Class III: High-risk devices, which must undergo rigorous premarket approval (PMA).
Most UVB therapy devices are classified as Class II, meaning that they must demonstrate substantial equivalence to a device already on the market. Manufacturers are required to submit a premarket notification, known as a 510(k), to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their devices.
FDA Clearance for UVB Therapy Devices
Numerous UVB therapy devices have received FDA clearance, indicating they meet the standards for safety and effectiveness. This includes both home-use and clinical phototherapy devices. Devices that are found to be substantially equivalent to an existing FDA-cleared device can be marketed for the treatment of specific conditions, including psoriasis and other skin disorders.
Examples of FDA-Cleared Devices
- Narrowband UVB Therapy Units: Many narrowband UVB lamps, designed for clinical and home use, have received FDA clearance. These devices emit a specific wavelength of UVB light that has been shown to be effective in managing psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other conditions.
- Handheld UVB Devices: Portable UVB units allow patients to administer treatment at home, providing convenience and accessibility. These devices also have received FDA clearance based on their safety and effectiveness.
Effectiveness of UVB Therapy
Numerous studies support the effectiveness of UVB therapy in treating various skin disorders. Research shows that UVB treatment can lead to significant improvements in symptoms, including reduced itchiness, scaling, and inflammation. For chronic conditions like psoriasis, UVB therapy is often considered a first-line treatment due to its ability to induce long-term remission in many patients.
Patient Outcomes and Safety
Patients undergoing UVB therapy typically experience a reduction in the severity of their symptoms within a few weeks of treatment. However, it’s essential to note that the success of the therapy can vary depending on factors such as skin type, the severity of the condition, and adherence to the recommended treatment schedule. Additionally, while UVB therapy is generally considered safe, potential side effects may include skin irritation, redness, and, with excessive exposure, an increased risk of skin cancer.
What Patients Need to Know
When considering UVB therapy as a treatment option, patients should be informed about a few key considerations:
Consult with a Dermatologist
Before starting UVB therapy, patients should consult with a qualified dermatologist who can assess their medical history, skin type, and specific condition to determine if UVB therapy is an appropriate treatment option. Dermatologists can also provide guidance on the most effective dosing schedule and treatment plans based on individual needs.
Understanding Treatment Duration and Frequency
Effective UVB treatment generally requires multiple sessions per week, with the total duration of treatment spanning several weeks to months. Patients should adhere to their treatment schedules to achieve optimal results.
Home vs. Clinical Therapy
Patients may have the option to undergo UVB therapy in a clinical setting or to invest in home-use devices. While clinical treatments are typically administered by professionals, home devices offer flexibility and may be more cost-effective over time. However, patients should be well informed about the safe and effective usage of home devices.
Conclusion
In summary, UVB therapy is an FDA-cleared treatment option for various dermatological conditions, entirely eligible for patients seeking effective management strategies for their skin issues. It offers a viable, non-invasive approach to reducing symptoms and improving the quality of life for many individuals suffering from skin disorders. As with any medical treatment, prospective patients should engage in thorough discussions with healthcare professionals to evaluate the suitability of UVB therapy for their specific needs, ensuring that they make well-informed decisions on their treatment pathways. As research and technology continue to advance, UVB therapy is expected to remain a cornerstone in the realm of dermatological treatments, providing hope and healing for countless individuals.