Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that leads to the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in scaling on the skin’s surface. The management of this condition has evolved significantly over the years, particularly with advances in UVB phototherapy, a treatment that involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet B light.
Recent technological innovations in UVB therapy aim to improve efficacy, safety, and patient compliance. This article delves into these latest developments and their implications for psoriasis treatment.
Understanding UVB Phototherapy
UVB phototherapy is a cornerstone treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis. It works by slowing down the excessive skin cell growth associated with the condition. Traditional UVB therapy is typically administered in a clinical setting, utilizing full-body or targeted light units to expose the affected skin to specific wavelengths of UVB light. While effective, traditional forms of UVB treatment can be inconvenient, requiring frequent visits to healthcare facilities.
Advancements in UVB Technology
1. Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) Therapy
One of the most significant advancements in UVB treatment is the development of narrowband UVB therapy. Unlike broad-spectrum UVB, which encompasses a wider range of wavelengths, narrowband UVB focuses on a specific wavelength (around 311-313 nm). Research has shown that narrowband UVB can lead to faster and more effective clearing of plaques, with fewer side effects compared to traditional methods. The improved targeting reduces the risk of burning and makes treatment sessions shorter, enhancing patient comfort and compliance.
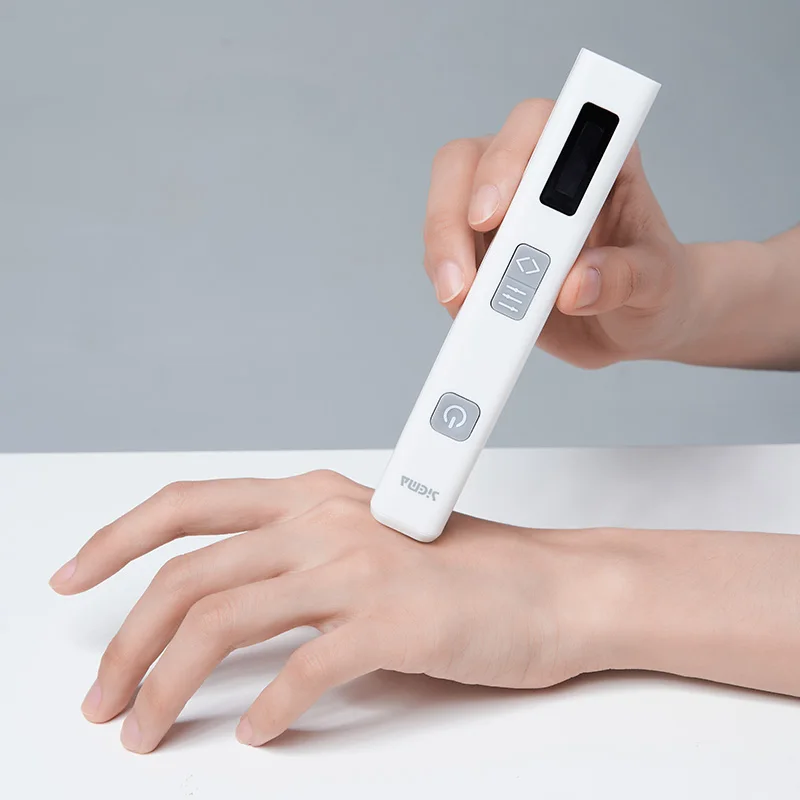
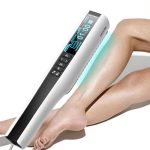
2. Home Phototherapy Devices
The rise of home phototherapy devices has revolutionized the management of psoriasis. These compact, portable units allow patients to undergo UVB therapy in the comfort of their homes. Recent innovations have enhanced the design and effectiveness of these units, with some devices resembling hand-held lamps or full-body cabinets that can be easily set up. These advancements promote greater adherence to treatment regimens, ensuring more consistent exposure to UVB light, which can lead to better long-term outcomes.
3. UVB Light Therapy with Digital Monitoring
Some of the latest UVB devices incorporate digital monitoring technologies that track dosage and exposure times. By utilizing smartphone applications, patients can receive reminders for treatment schedules and monitor their progress. This integration of technology enhances patient engagement and education, allowing individuals to take an active role in managing their condition. Moreover, healthcare providers can access this data to make informed adjustments to treatment plans, promoting personalised care.
Safety Innovations in UVB Treatment
Safety is a paramount concern in UVB phototherapy, as overexposure can lead to skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. To address these issues, several innovations have emerged.
1. Enhanced Protective Measures
Modern UVB devices often feature built-in safety mechanisms such as automatic shut-off timers and UV shields that protect unexposed skin areas. Some new units are designed to block out harmful wavelengths while selectively allowing therapeutic light to penetrate the skin. These protective measures reduce the risk of adverse reactions and improve the overall safety of treatment.
2. Combination Therapies
Research has increasingly focused on the benefits of combining UVB therapy with systemic treatments or topical agents. This multimodal approach can enhance the effects of UVB while minimising the dose required, further improving safety. For instance, combining NB-UVB therapy with biologic medications or retinoids has shown promising results, leading to more significant and quicker improvements in psoriatic lesions.
Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
The advent of telemedicine has changed the landscape of healthcare, allowing for remote consultations and follow-ups for patients undergoing UVB therapy. This is particularly beneficial for those living in remote areas or those with mobility issues. Virtual appointments enable healthcare providers to assess treatment response, manage side effects, and adjust regimens without the need for in-person visits. This ease of access may also improve treatment adherence as patients can easily communicate their progress and concerns.
Conclusion
The advancements in UVB technology for psoriasis treatment usher in a new era of effective and patient-centred care. Narrowband UVB, home phototherapy devices, and digital monitoring not only enhance treatment efficacy but also improve patient compliance and safety. As research continues to explore the full potential of UVB therapy and its combinations with other treatments, those living with psoriasis will likely experience significant improvements in their quality of life. The integration of digital health solutions further supports this evolution, empowering patients to take control of their condition. Ultimately, the newest technologies in UVB treatment provide hope for a future where psoriasis management is more accessible, efficient, and effective.